Flowering
plants reproduce sexually.
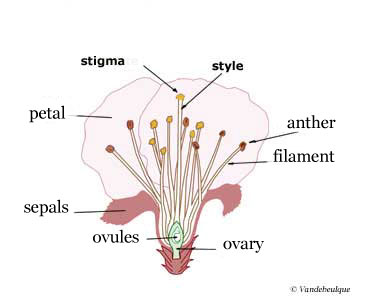
Pollination is the transfer of pollen (male gametes) to the stigma
(entry to the female reproductive system).
Apple and pear flowers are hermaphrodite, that is they contain both male
and female organs.
The male organ is the stamen, comprising the filament, at
the end of which, the anther contains the pollen.
The female organ is the pistil, comprising the ovary, containing
the ovules and protected by the sepals. The ovary extends into a long
tube, the style ending in a sticky bulge that traps the pollen
: the stigma.
Even though apple flowers are hermaphrodite (like most rosaceae), they
are not, with very few exceptions, self-pollinating.
The apple tree has 17 pairs of chromosomes. Some varieties are diploid,
so they have 2 n chromosomes ; other varieties are triploid with 3 n chromosomes.
Diploids are self-pollinating. It is almost impossible for triploids
to be self-pollinating (Rambour d'Hiver, Reinette du Canada…), so they
need pollen from diploids.
Among diploids, certain varieties are very rich in good quality pollen
and their presence is strongly recommended : Malus Evereste, Belle Fleur
Jaune, Reine des Reinettes, Transparente de Croncels, Pomme Cloche, etc.
We also need a vector to carry the pollen from one plant to another.

- the wind. It carries pollen randomly in all directions
- insects, particularly bees, who swallow the nectar and collect the pollen that they partially disperse when they pass from flower to flower.
The case of the mason bee : Osmia rufa and Osmia cornuta.
This very furry little bee builds odd tubular constructions to rear their larvae. It presents several advantages over our domestic bee : thanks to its abundant "fur" it accumulates more pollen and spends much less time cleaning itself. Also, it starts work earlier in the season, ensuring the pollination of early varieties. Lastly, it is present even if there are no hives in the vicinity.
It can be encouraged if you leave at its disposal a bundle of tubes in which it likes to lay its eggs. These can be bought in specialized stores and their structure is such that access is difficult for osmia parasites.
.


Osmia Cornuta
For an abundant crop, you must encourage pollination.
Always plant diploid varieties near triploids.
It is a good idea to create herbaceous flower-beds in the orchard, and also to plant hedgerows that serve as refuge to all auxiliary pollen vectors.